
Redefining networks: Navigating the world of SD-WAN
In the ever-evolving landscape of enterprise networking, businesses are constantly seeking efficient solutions to connect their diverse set of locations, data centres and remote users. The traditional approach to networks has started to show limitations, as the increasing speed and scale of diversity have created the need for a more efficient, reactive and comprehensive solution.
Software-Defined Wide Area Network (SD-WAN) offers a dynamic and intelligent architecture that blends the power of the internet with the reliability of private Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS).
Let's delve into the key aspects of SD-WAN, from its architecture to the role managed network providers can play.
The bridge between networks
The growing geographic disparity between employees is posing a challenge for many organisations. Gartner's 2023 Forecast Report predicted that up to 39% of the workforce would be hybrid by the end of the year, and this number is only set to increase.
Organisations managing thousands of customers, offices and employees are looking for every opportunity to optimise costs and enhance the overall network experience for users.
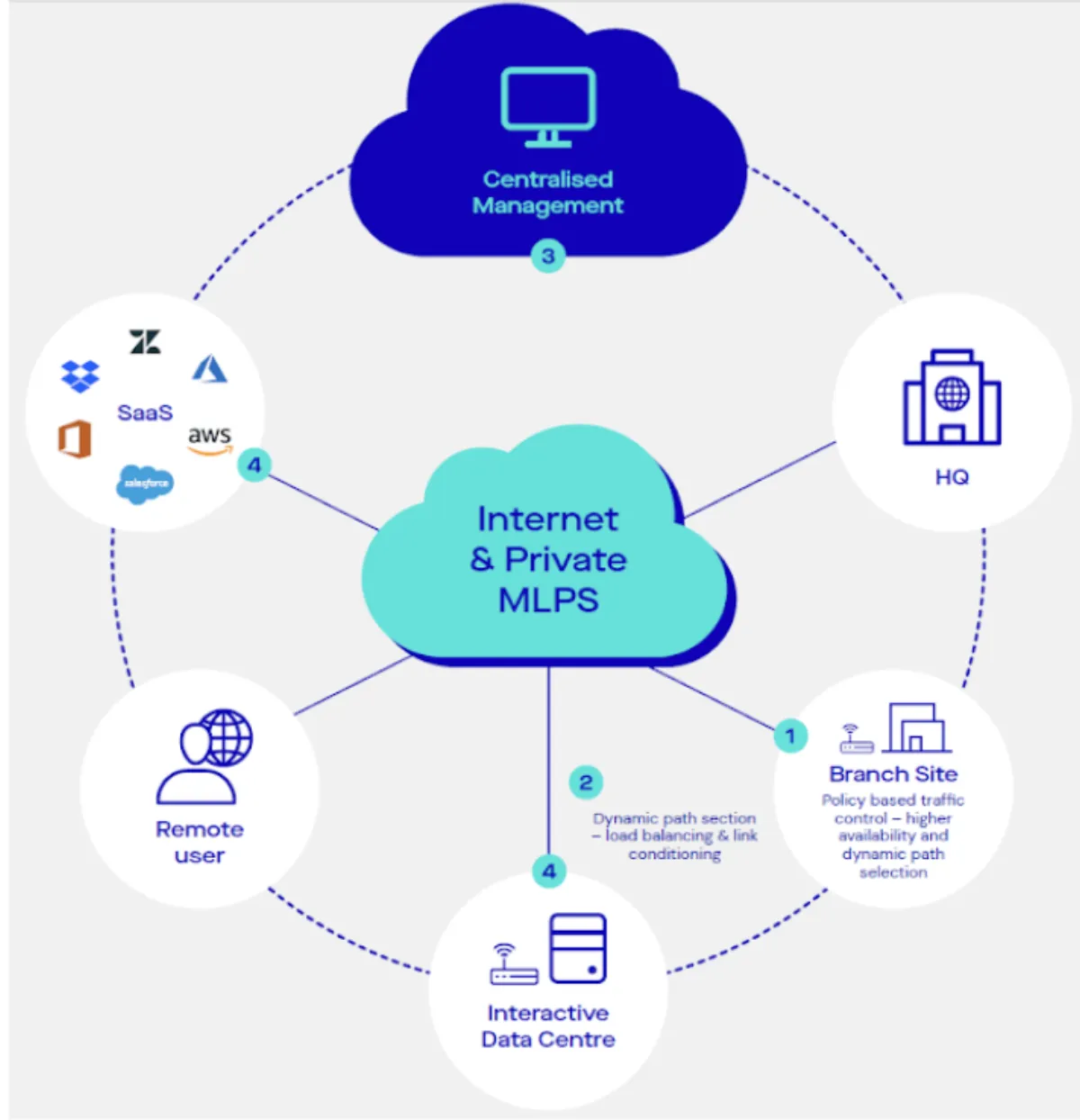
SD-WAN helps achieve exactly that, as it's designed to manage the connectivity between an organisation's headquarters, branch offices, data centres and remote users. With an intelligent approach to wide area networking, SD-WAN steers traffic over multiple connection types, including public internet and private MPLS links, to ensure optimal performance.
In the traditional networking setup, organisations often relied on expensive and dedicated MPLS connections to ensure reliable data transmission between locations, employing fixed quality of service (QoS) profiles to prioritise traffic. SD-WAN, however, introduces an innovative approach by utilising dynamic policy-based traffic controls and incorporated edge security. Combined with the ability to run over the internet or MPLS links, this centralises management and can reduce costs while leveraging the full potential of both technologies.
There are six major differences SD-WAN brings to the table:
1. Centralised control and orchestration: One of the key features of SD-WAN is centralised control and orchestration. This aspect allows administrators to manage, monitor and control the entire network on a single pane of glass. It provides a holistic view of the network, enabling administrators to set policies, prioritise traffic, allocate bandwidth and enforce security measures across all locations. This centralised management streamlines network administration and ensures consistent policy enforcement.
2. Dynamic path selection: SD-WAN architecture dynamically selects the optimal path for data traffic based on real-time conditions. It considers factors like bandwidth utilisation, availability, latency, jitter and packet loss. By dynamically steering traffic, SD-WAN ensures critical applications receive the necessary bandwidth, while less important traffic can be routed through less expensive or congested connections. This approach enhances application performance and user experience.
3. Hybrid connectivity: A core strength of SD-WAN architecture lies in its ability to support multiple types of connections. This typically includes a mix of public internet links, like broadband and private MPLS links. The hybrid connectivity approach allows organisations to harness the cost-effectiveness of internet links while maintaining the reliability and security of MPLS. This ensures that businesses can optimise their network costs without sacrificing performance.
4. WAN optimisation: SD-WAN includes built-in WAN optimisation techniques. These techniques help to mitigate issues such as latency, jitter and packet loss, especially over long distances. WAN optimisation features can include data compression, caching, and protocol optimisation, all of which contribute to improved application performance and a smoother user experience.
5. Security integration: Security is a crucial aspect of any network architecture, and SD-WAN is no exception. Many SD-WAN solutions include integrated security features. These may include encryption for data transmitted over the network, firewall capabilities, intrusion detection and prevention, and other security measures. The ability to enforce security policies across all network connections helps organisations maintain a consistent security posture.
6. Application-aware routing: SD-WAN architecture is application-aware, meaning it can recognise the specific applications being used on the network. This awareness allows administrators to prioritise critical applications to ensure they receive the necessary bandwidth and reduce the impact of non-critical applications on the network.
The Role of Managed Network Providers
Managed network providers, such as Australian technology provider Interactive, play a pivotal role in unlocking the full potential of SD-WAN. Their expertise and experience in deploying and managing complex network infrastructures ensure a smooth transition to SD-WAN. These providers work closely with organisations to design and implement tailored SD-WAN solutions that align with specific business requirements.
It's not about a one-size-fits-all solution, though – managed service providers need to understand that each organisation has unique networking needs. That's why Interactive offers tailored solutions, optimising performance and cost savings.
The continuous support offered by managed network service providers is key to unlocking the potential of this new technology; SD-WAN requires ongoing monitoring, management and updates. Managed network providers offer 24/7 support, ensuring the network operates at peak efficiency.
The transformative power of SD-WAN is undeniable. It enables organisations to streamline their network infrastructure, improve performance, reduce costs and enhance overall business efficiency. If that's something you want for your organisation, book a complimentary assessment with Interactive's Software-Defined Networks Lead, Andrew Robson, here.

